A rare diagnosis of right iliac fossa pain syndrome - appendiceal mucocele
Image Description
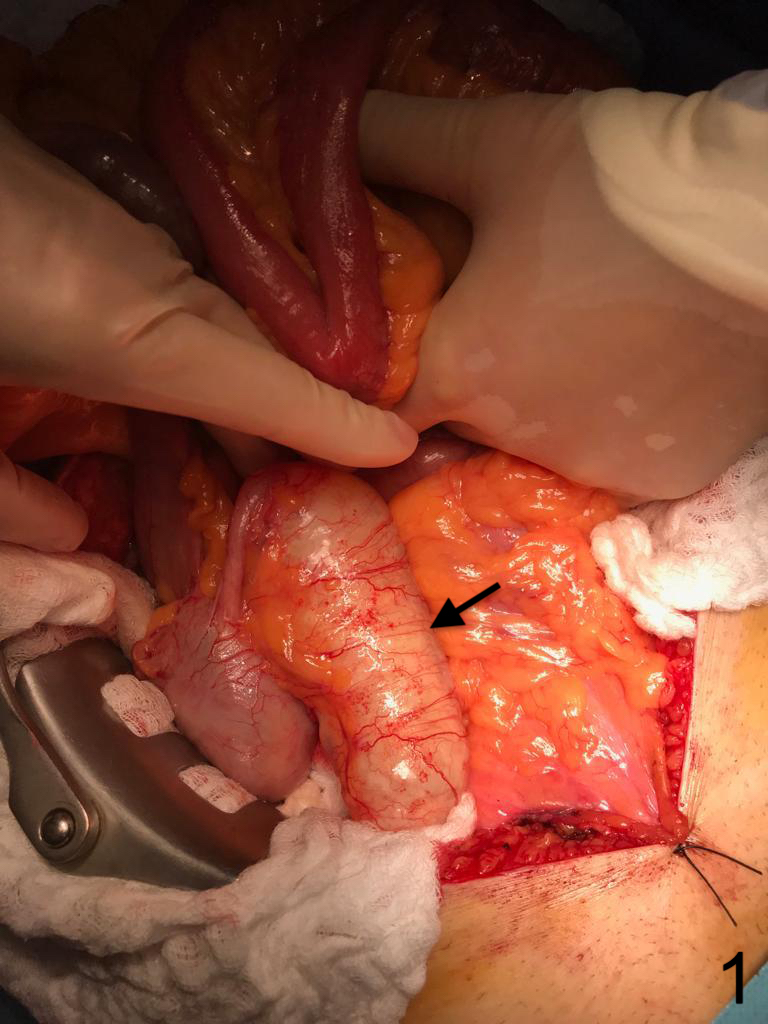
The Appendiceal mucocele represents a rare pathology of the appendix encountered on average in only 0.2% of patients. It is more common in women with an average of 3:1 compared to men. These tumors are mucus-producing and frequently give rise to mechanical obstruction of the appendicular base by enlargement of the appendix wall, thus, generating a chronic accumulation of mucus and an increase in appendix size up to possible wall rupture (Figure 1). When such a tumor is identified, the patient requires in-depth investigations, as these tumors are associated with other colon and ovarian secreting mucus cancer. The macroscopic aspect of these tumors is of a diffuse enlarged and elongated appendix with a smooth surface and fluctuation upon palpation ( do to the intraluminal mucus accumulation) and without signs of infection, local inflammation or adherences. The elective treatment is the surgical resection - ideal laparoscopic appendectomy. If the base of implantation of the appendix is wide a the right ileocolectomy is recommended. In our case do the small base a simple appendectomy was practiced. The histopathological results confirmed the diagnosis of an Appendiceal mucocele (pTis) which was limited to the muscularis propria (curative intervention).