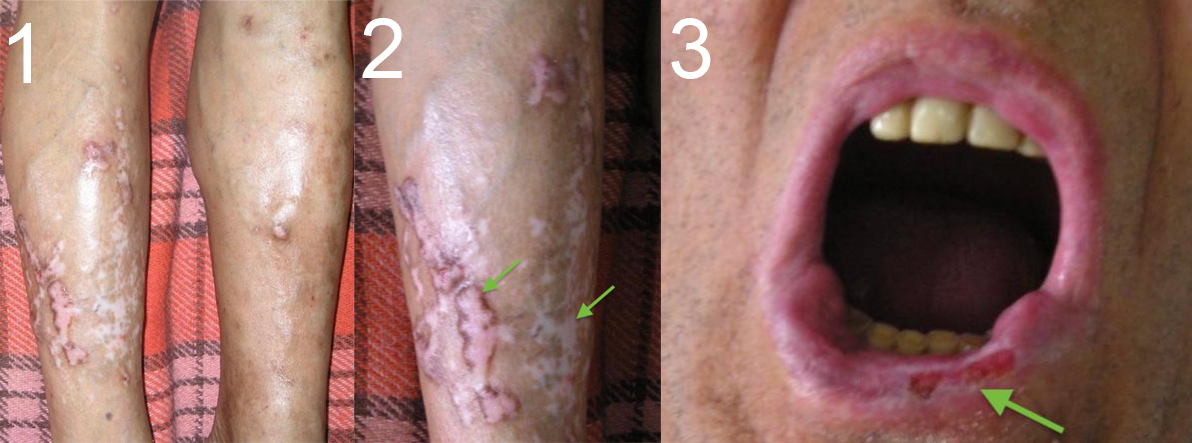
Lichen planus associated with chronic active hepatitis C
Image Description
Lichen planus is characterized by flat-topped violaceous pruritic papules with a generalized distribution.
We present the case of a 36-year-old patient diagnosed with chronic active hepatitis C 5 years ago, that associates lichen planus lesions. By inspecting the lower limbs, we observed multiple skin lesions, causing severe itching. These appeared purplish-coloured, with white streaks over and flat tops more pronounced in the lower right limb. The patient also complained of painful soreness caused by lacy-white lesions of the mouth (Fig. 1-3).
Lichen planus can be seen in patients with a variety of liver diseases, particularly advanced liver disease. Systematic reviews have shown that patients with oral lichen planus are approximately two to six times more likely to have reactive anti-HCV antibodies compared with the normal population, although there is substantial geographical heterogeneity to the findings [1]. In a list of studies, the prevalence of anti-HCV antibodies in patients with lichen planus ranges from 10% to 40% [2]. There is evidence of a genetic risk for HCV-associated lichen planus [3].
Because of the frequency with which HCV (hepatitis C virus) infection has been reported among patients with lichen planus in some geographic locations, we advise testing for HCV in patients with lichen planus.
References
Alaizari NA, Al-Maweri SA, Al-Shamiri HM, et al. Hepatitis C virus infections in oral lichen planus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Aust Dent J 2016; 61:282.
Gumber SC, Chopra S. Hepatitis C: a multifaceted disease. Review of extrahepatic manifestations. Ann Intern Med 1995; 123:615.
Nagao Y, Nishida N, Toyo-Oka L, et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Risk Variants for Lichen Planus in Patients With Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017.